Comparing TR calls across different parameter sets
Tools used: compareSTR
This vignette shows how to use compareSTR to compare two VCF files generated using the same set of reference TRs. In this example, we use VCF files c57_ex1.vcf.gz and c57_ex2.vcf.gz available at https://github.com/gymrek-lab/TRTools/tree/master/example-files. These VCF files were generated by GangSTR on a mouse dataset using two different sets of stutter parameters.
To run compareSTR:
compareSTR \
--vcf1 c57_ex1.vcf.gz \
--vcf2 c57_ex2.vcf.gz \
--vcftype1 gangstr \
--vcftype2 gangstr \
--out c57-compare \
--stratify-fields DP \
--stratify-binsizes 0:50:10 \
--bubble-min -10 --bubble-max 10
Let’s go through what each option did:
--vcf1and--vcf2give the name of the two VCF files being compared.--vcftype1and--vcftype2give the types of the two VCF files being compared--outis the required output prefix.--stratify-fields DPand--stratify-binsizes 0:50:10tell the script to compute overall concordance metrics stratifying by the DP field (coverage) in bins of 10 ranging from 0 to 50. Since we didn’t specify which file to apply the stratification to with--stratify-file, it gets applied to both.--bubble-min -10 --bubble-max 10give the axis range of the bubble plot to show (see below).
This will output a number of files. We’ll peek at a couple of them.
c57-compare-overall.tabwill give overall concordance info:period DP concordance-seq concordance-len r2 numcalls ALL NA 0.9760415527610716 0.9760415527610716 0.9909303005952199 91450 ALL 0.0-10.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 266 ALL 10.0-20.0 0.9426900584795321 0.9426900584795321 0.9995028621738471 855 ALL 20.0-30.0 0.9285714285714286 0.9285714285714286 0.9950024662641009 1218 ALL 30.0-40.0 0.9548577036310107 0.9548577036310107 0.9780821396586636 3057 ALL 40.0-50.0 0.9739065606361829 0.9739065606361829 0.9880478071563313 8048
Here, the first line gives the overall concordance. The lines below are stratified by DP value. For each set, the concordance (percent of calls matching), r2 (Pearson correlation between allele calls), and number of calls in each group is shown.
c57-compare-callcompare.tabgives a call by call comparison, which is useful for looking at exactly which loci/sample calls were discordant.c57-compare-locuscompare.tabandc57-compare-samplecompare.tabgive locus and sample level concordance. In this case these are not very interesting since we have only one sample being compared. But in other settings, these files can be used to identify poorly performing samples or loci.c57-compare-bubble-periodALL.pdfplots the genotypes in file 1 vs. file 2. Genotypes are given in terms of the sum across both alleles of the repeat units different from the reference. Bubble sizes give the number of calls represented by each point. This plot is shown below:
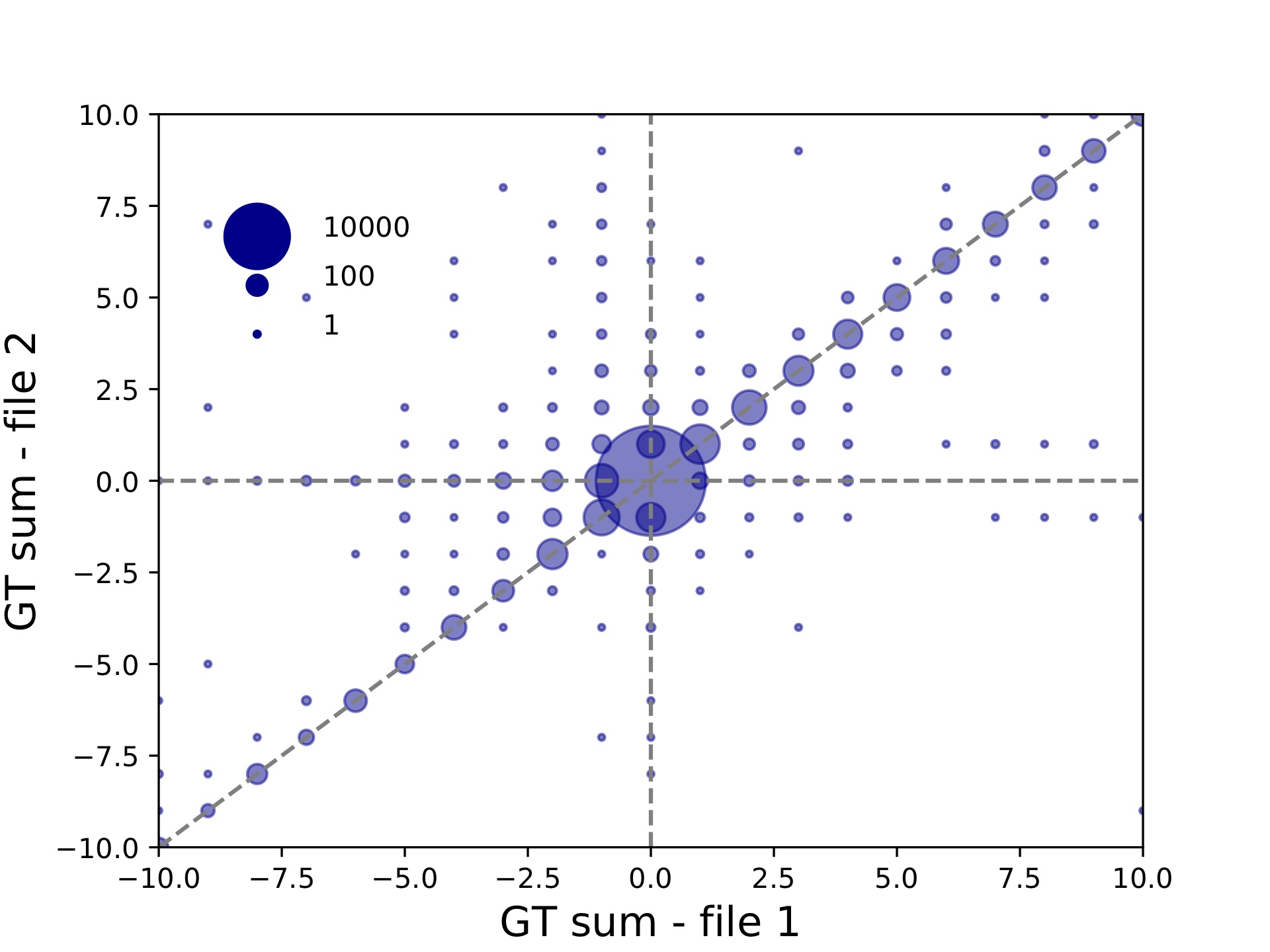
Since we used --bubble-min -10 --bubble-max 10, the plot goes only from -10 to +10. This plot can be useful in evaluating the effects of varying different parameters on calling. For example, we can see from this plot that there are quite a few calls that are called longer in file 2 vs. file 1.